Until the service is performed or the good is delivered, the company is indebted to the customer, making the revenue temporarily a liability. Once earned, the revenue is no longer deferred; it is realized trial balance and counted as revenue. In other words, the payment received is for goods or services that will be delivered at some point in the future. As a result, the company owes the customer what was purchased, and funds can be reclaimed before delivery. Managing unearned fees affects cash flow by influencing the timing of cash inflows and outflows. Payments for undelivered services provide immediate cash, enhancing liquidity.
Is deferred revenue a liability?

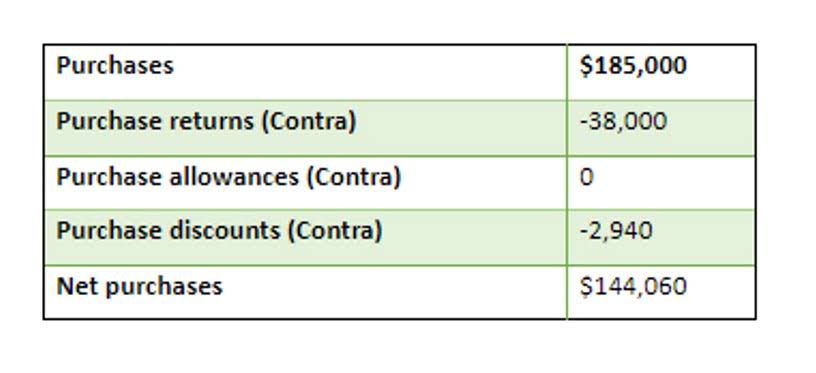
Current assets are receivables that a company will get within a year. Generally, they are transactional where money is exchanged for is unearned revenue a current liability a service/good in real-time. Unearned revenue is listed under “current liabilities.” It is part of the total current liabilities as well as total liabilities. A client purchases a package of 20 person training sessions for $2000, or $100 per session.
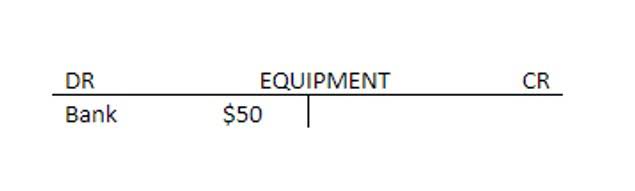
Impact on Cash Flow
Typically, this value is shown as a current liability on the balance sheet of the company. But that again depends on the period within which the goods should be delivered. If the delivery date is extended beyond 12 months after the transfer of the revenue, then it will be recorded under long-term liability. Deferred revenues are the payments received by customers for goods or services they expect to receive in the future.
- As mentioned, accounting standards do not allow companies to record unearned revenues as income.
- It will be recognized as income only when the goods or services have been delivered or rendered.
- Baremetrics is a business metrics tool that provides 26 metrics about your business, such as MRR, ARR, LTV, total customers, and more.
- The liability exists until the company performs its contractual duties or provides the products or services, at which point the unearned revenue is recognized as earned revenue and the liability is reduced.
- After a month, ABC Co. sells $10,000 worth of goods to XYZ Co. against the amount received in advance.
Service retainers paid in advance
The customer chooses to pay the full amount before the work starts, so the income is recorded as a $500 debit in the cash account Accounting for Churches and a $500 credit in the ‘unearned revenue’ account. Two weeks later, when the project is finished, the business makes an adjusting entry, which debits $500 from the unearned revenue account and credits the revenue account $500. Both refer to payments received for products or services to be delivered in the future. These payments are recorded as liabilities until the goods or services are provided, at which point they are recognized as revenue. The person receives the money from one party for which the goods have been delivered, or the services have been rendered to the party.
What Is Unearned Revenue and How to Account for It
This transition is crucial, as it moves the revenue from a liability to an asset – specifically, from unearned revenue to earned revenue. Unearned revenue is only recognized whenever a company has a contract with a client that necessitates the provision of a certain product or service. The contract also has to highlight whether the obligation is subscription-based and if the client has to make advance payments. Unearned revenue is not an uncommon liability; it can be seen on the balance sheet of many companies. A credit memo states the customer no longer owes towards the contract. In the same breath, the seller no longer owes services or products.
